
Self-hosting NocoBase on Ubuntu with PostgreSQL
 Atakan Öztarak
Atakan ÖztarakWant to use NocoBase as your no-code platform but prefer to keep everything on your own infrastructure? By self-hosting NocoBase on Ubuntu with PostgreSQL, you get unlimited users, full data privacy, and zero per-seat fees!
Looking for something simpler? If you'd rather skip server management and deploy NocoBase in under 5 minutes for €9/month, check out our guide on self-hosting NocoBase the easy way using Sliplane.
What is NocoBase?
NocoBase is an open-source, no-code/low-code development platform built on a plugin-based architecture. Think WordPress, but for business applications. You can build CRMs, project trackers, inventory systems, and pretty much any internal tool without writing a single line of code. The community edition is completely free.
What is NocoBase used for?
Teams use NocoBase to build custom business applications without coding. Common use cases include:
- CRM systems: manage contacts, deals, and sales pipelines
- Project management: track tasks, milestones, and team workloads
- Inventory management: monitor stock levels, orders, and suppliers
- Internal tools: build approval workflows, HR portals, and data dashboards
- Data collection: create forms, surveys, and data entry interfaces
If your team needs custom internal tools but doesn't have the developer resources to build them from scratch, NocoBase is built exactly for that.
NocoBase Pricing: Why Self-Host?
Most no-code platforms charge per user, which adds up fast as your team grows. Here's how much businesses typically spend on no-code platforms:
| Service | Starting Price | Users Included | Open Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retool | $10/user/month | Per seat | No |
| Airtable | $20/user/month | Per seat | No |
| Budibase Cloud | $50/month | 5 | Yes (OSS) |
| NocoDB Cloud | $20/month | Per seat | Yes (OSS) |
| Self-hosted | ~€3-5/month | Unlimited | Yes |
By self-hosting, you pay only for the server, typically €3-5/month on Hetzner, and get unlimited users, unlimited apps, and full control over your data.
NocoBase Alternatives
Before committing, it's worth comparing NocoBase with other popular no-code platforms:
- NocoDB: spreadsheet-style database interface (Airtable alternative), great for simple data management but no app builder
- Budibase: open-source low-code platform, good for internal tools but lacks NocoBase's plugin architecture
- Retool: powerful but proprietary and expensive, best for developer-heavy teams
- Appsmith: open-source, developer-focused, requires more coding than NocoBase
NocoBase stands out because of its WordPress-like plugin architecture. Instead of being locked into a fixed feature set, you can install or build plugins to add exactly what you need.
Prerequisites
Follow along this guide to learn how to deploy your own NocoBase instance on Ubuntu 24.04 using Docker, PostgreSQL, and Caddy Web server for automatic HTTPS.
Before we start, make sure you have:
- A Hetzner account (or any other cloud provider)
- Basic SSH experience
- An SSH key pair on your local machine
Step 0: Create a Server on Hetzner
First, we need to create an Ubuntu server. Log into your Hetzner Cloud Console and click the Create Resource button in the top right corner.
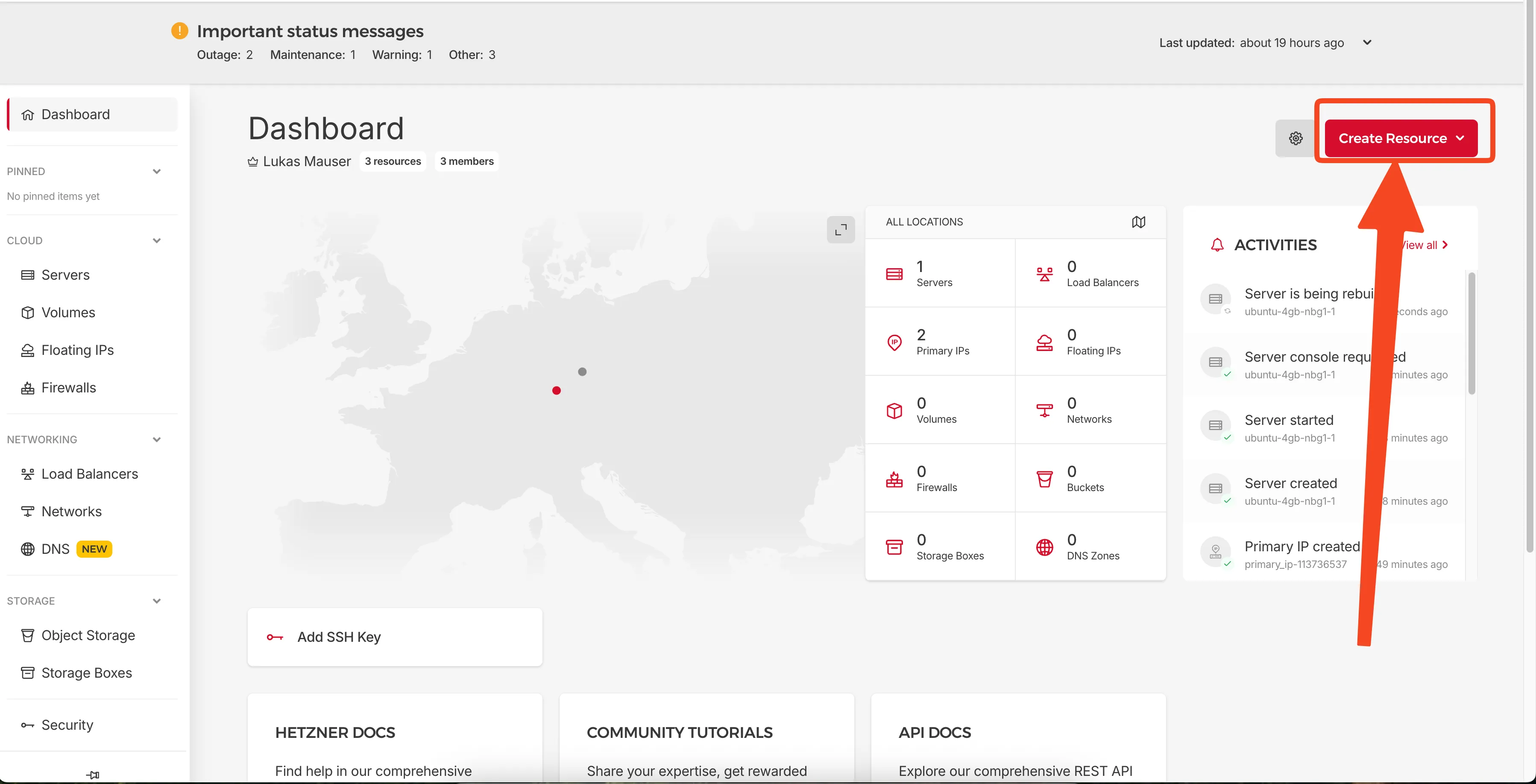 Click "Create Resource" to start creating your server
Click "Create Resource" to start creating your server
Select Server Type
Choose Shared Resources and select Cost-Optimized. For NocoBase, the CX23 server (2 vCPU, 4GB RAM, 40GB SSD) is a solid choice at just €2.99/month. NocoBase with PostgreSQL runs comfortably on 4GB RAM.
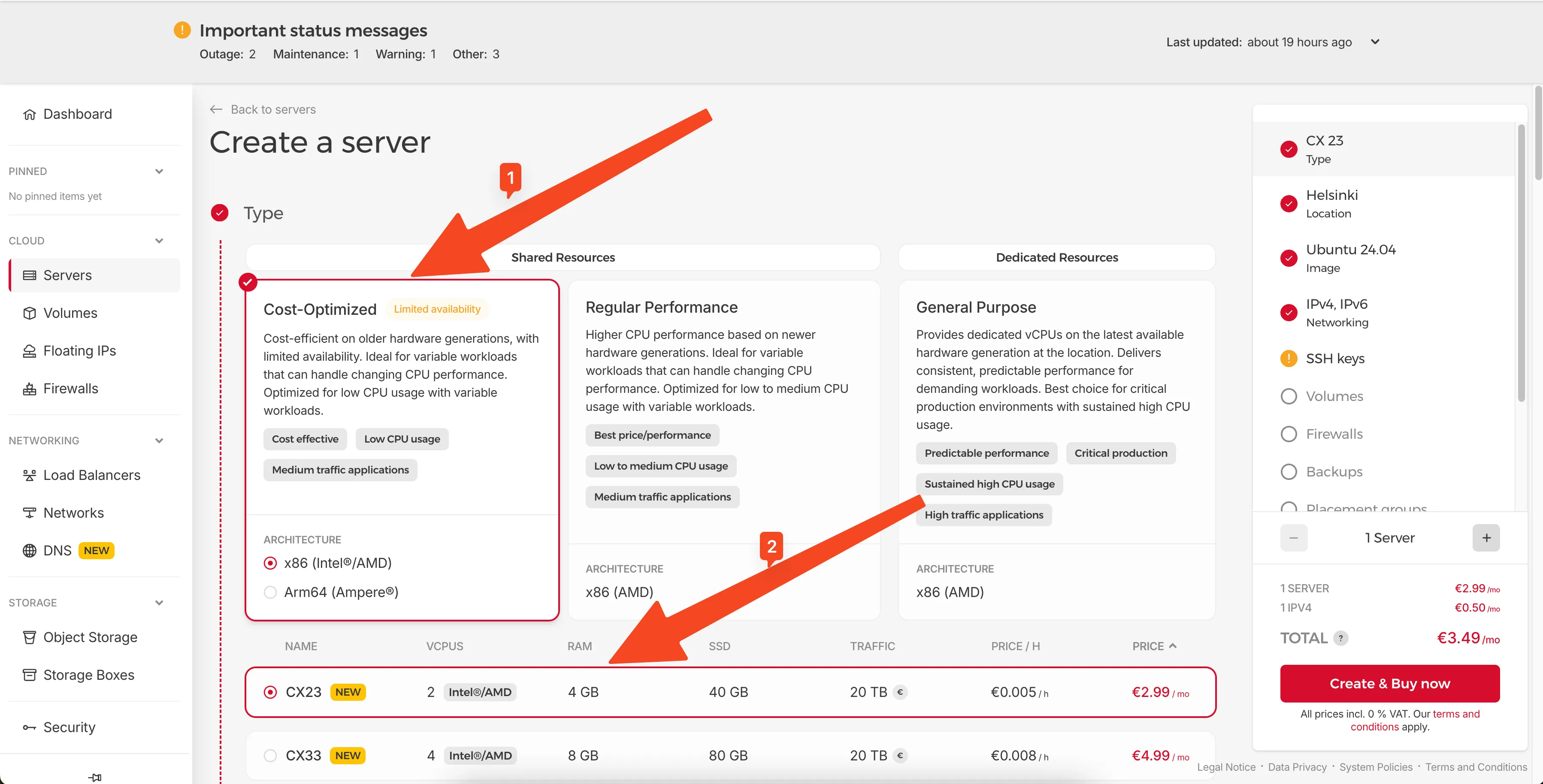 Select Cost-Optimized and CX23 server type
Select Cost-Optimized and CX23 server type
Select Location and OS
Choose a location close to your users (e.g., Nuremberg for EU) and select Ubuntu 24.04 as the operating system.
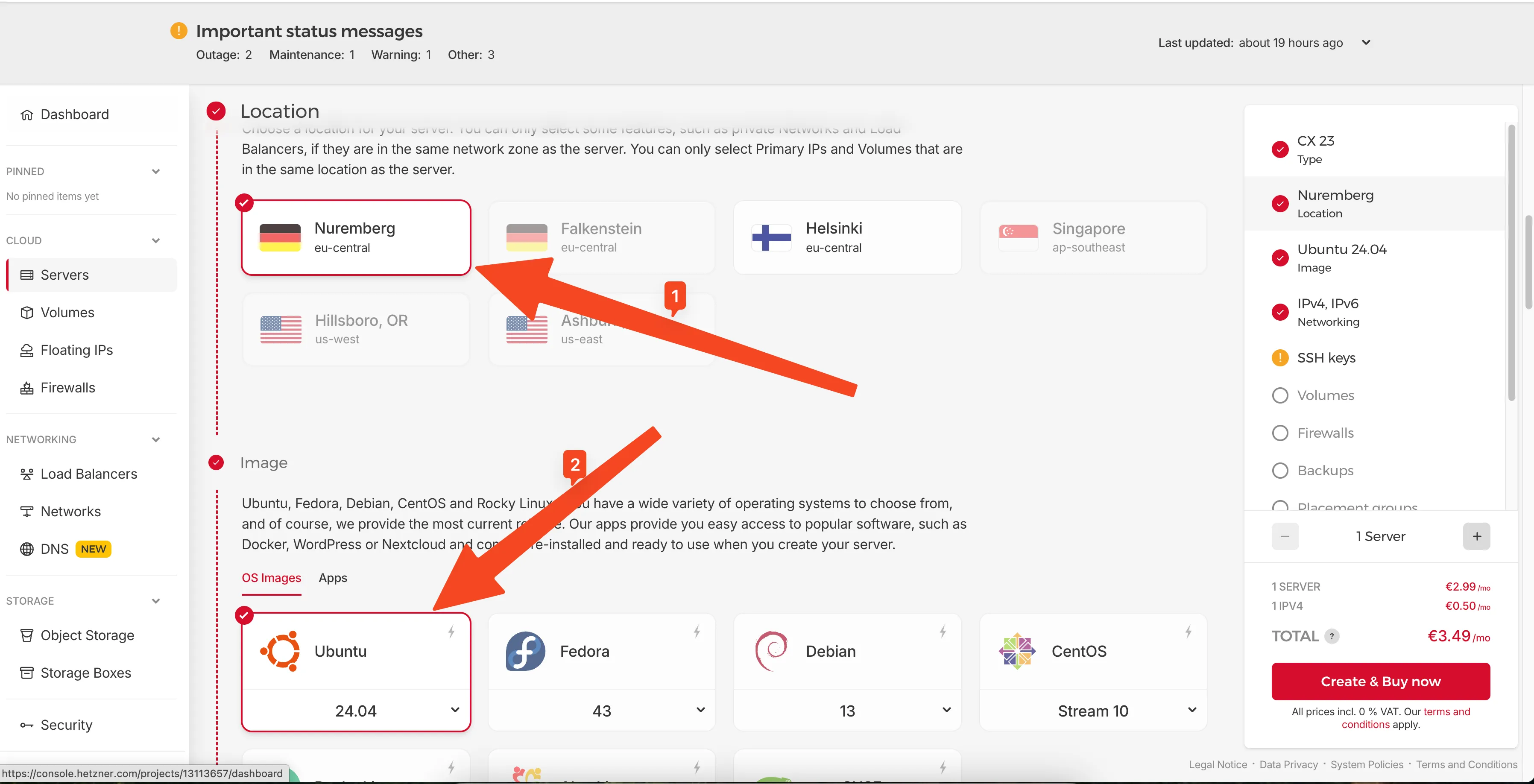 Choose your preferred location and Ubuntu 24.04
Choose your preferred location and Ubuntu 24.04
Add Your SSH Key
You'll need to add your SSH public key to access the server. On your local machine, copy your public key to clipboard:
# On macOS
pbcopy < ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub
# On Linux
cat ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub
# Then copy the output
 Copy your SSH public key from terminal
Copy your SSH public key from terminal
In the Hetzner console, click Add SSH Key and paste your public key. Give it a recognizable name.
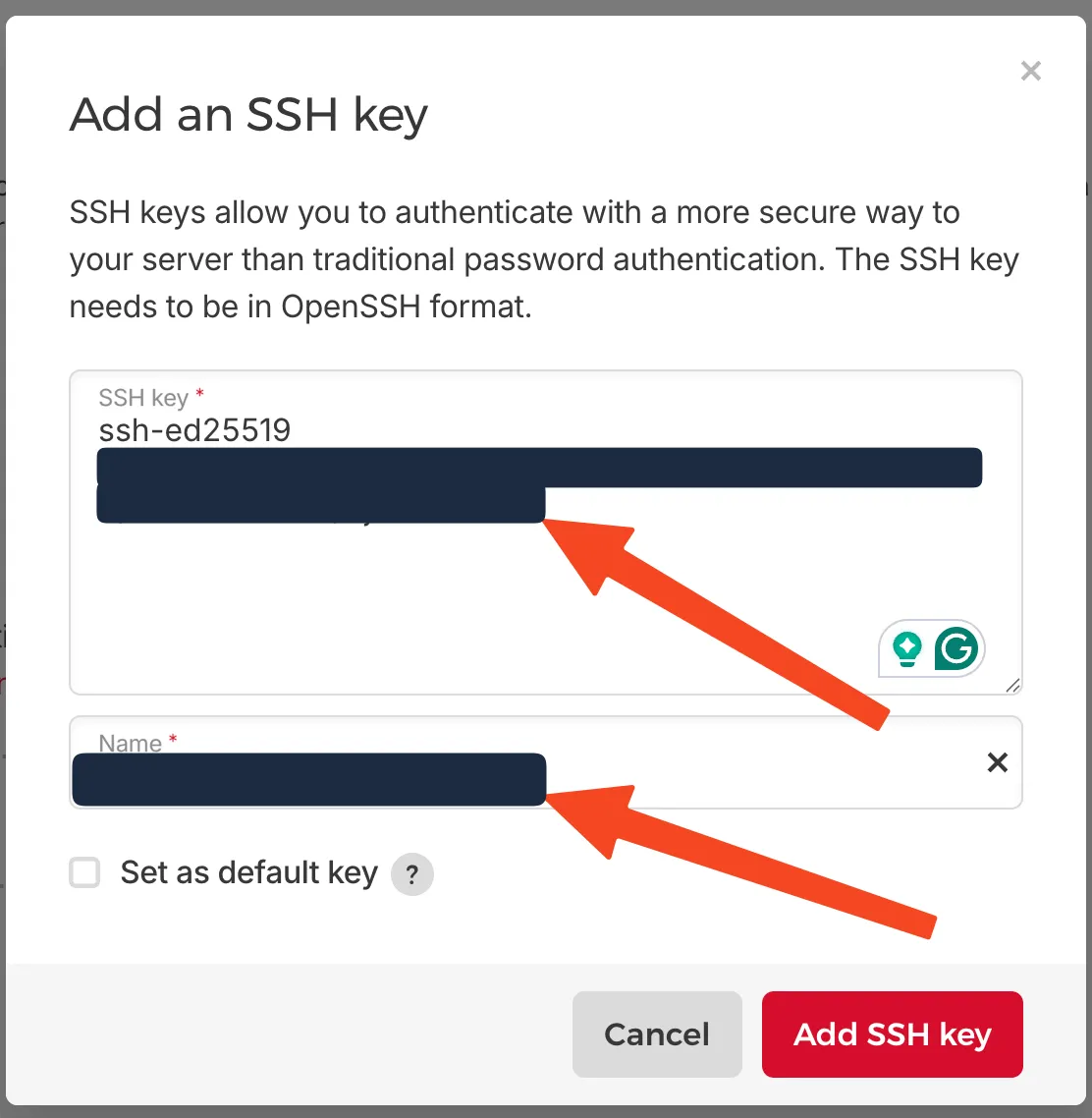 Paste your SSH key and give it a name
Paste your SSH key and give it a name
Create the Server
Give your server a name and click Create & Buy now.
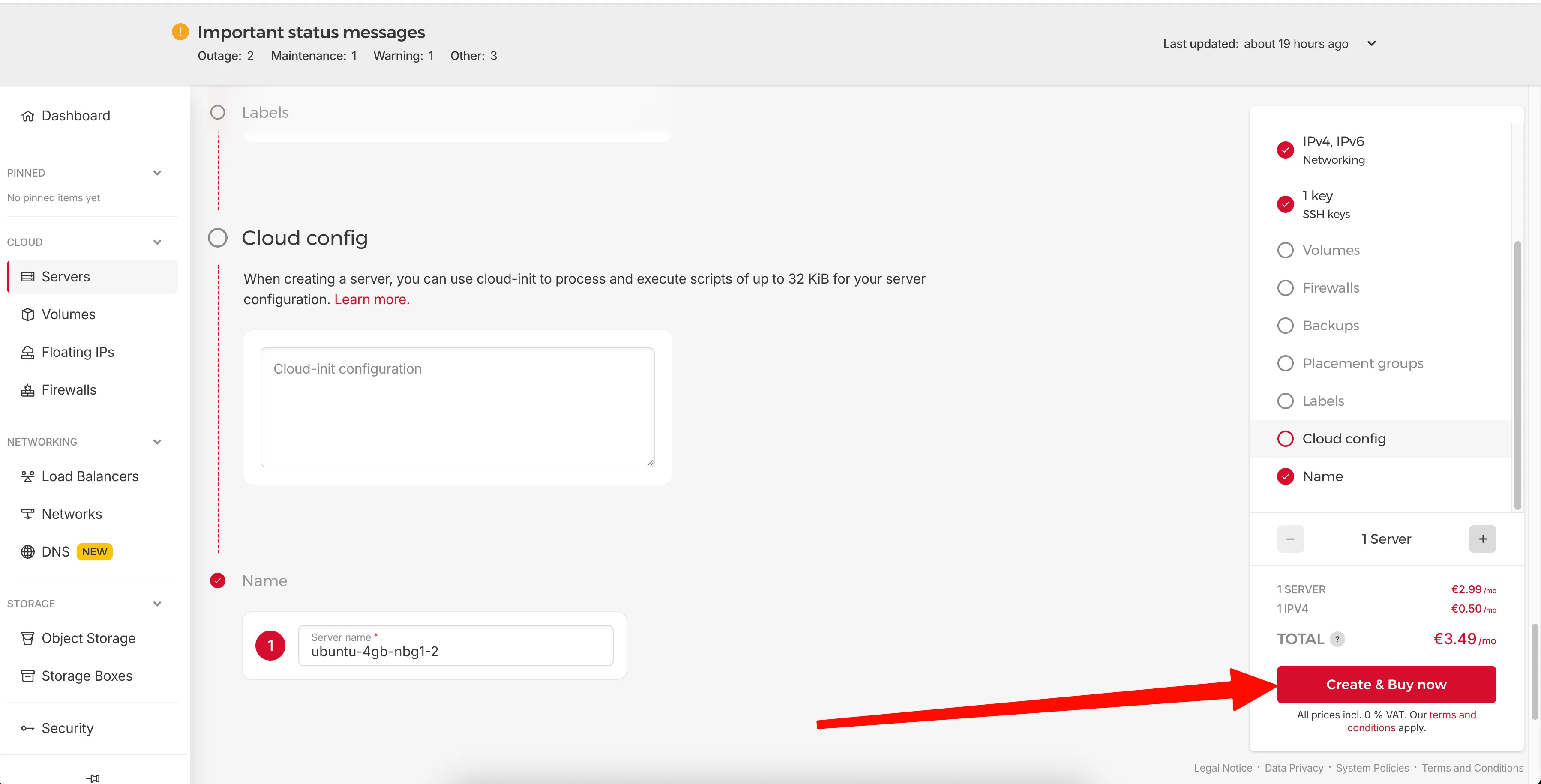 Name your server and click Create & Buy now
Name your server and click Create & Buy now
Get Your Server IP
Once created, you'll see your server's IP address in the overview. Copy this IP - you'll need it to connect via SSH.
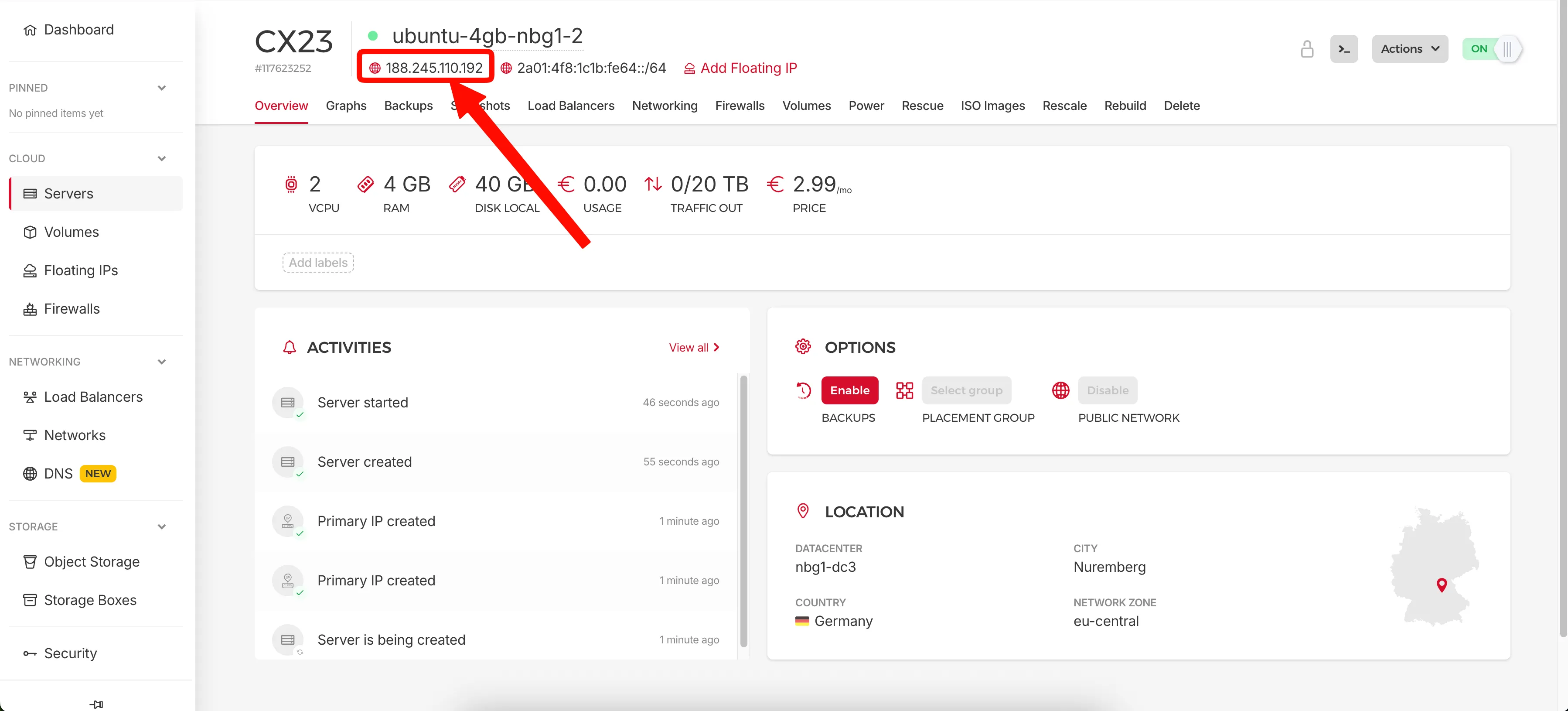 Copy your server's IP address
Copy your server's IP address
Connect via SSH
Now connect to your server using SSH:
ssh root@YOUR_SERVER_IP
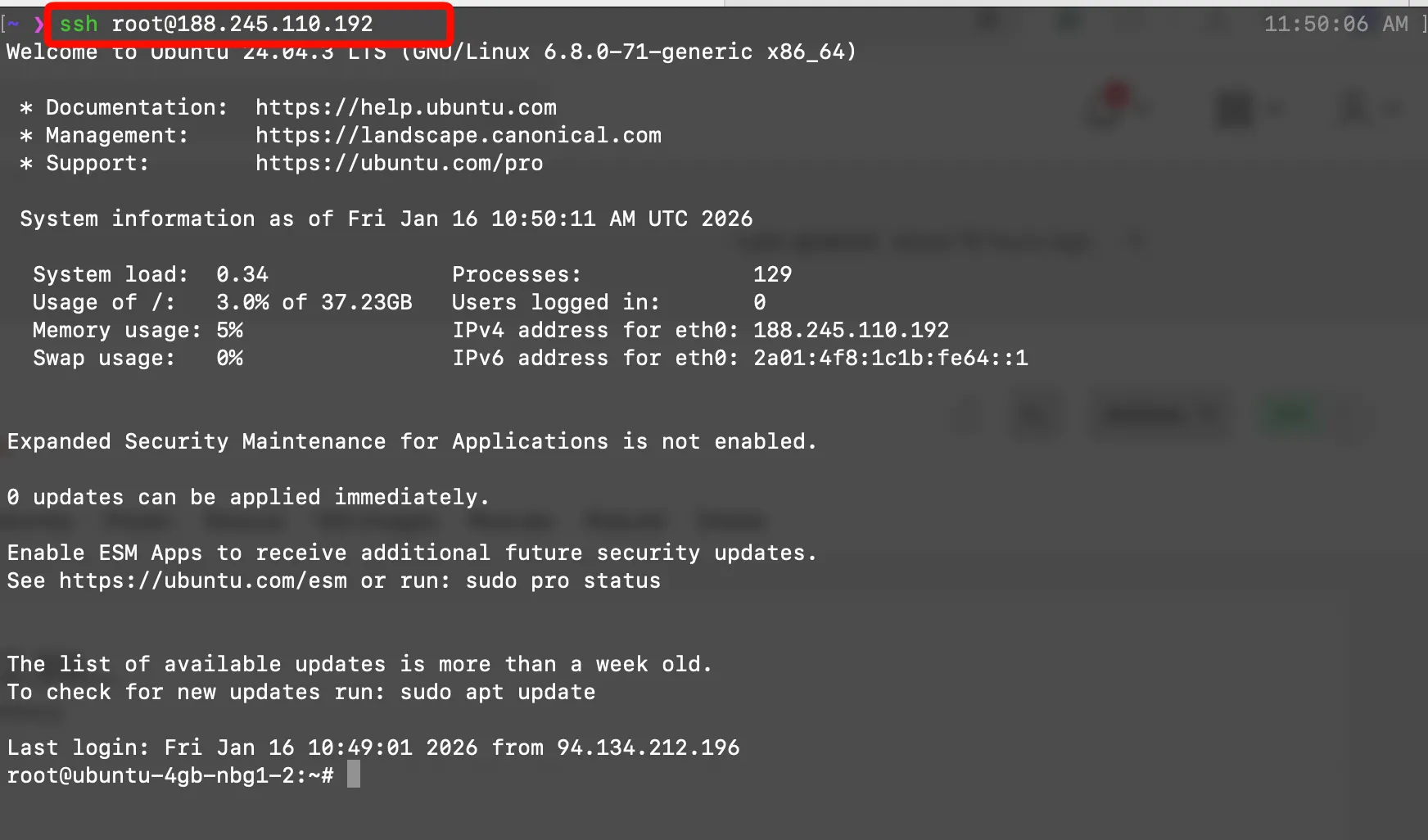 Successfully connected to your Ubuntu server
Successfully connected to your Ubuntu server
Step 1: Update Your Server
Once logged in, update the system to ensure it has the latest security patches and updates.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade -y
Once finished, your server is ready for installing the software.
Step 2: Install and Configure UFW Firewall
Only keep necessary ports open: SSH (22), HTTP (80), HTTPS (443).
Install UFW and configure the firewall as follows:
sudo apt install ufw -y
sudo ufw allow 22 # SSH
sudo ufw allow 80 # HTTP
sudo ufw allow 443 # HTTPS
sudo ufw enable
Check your firewall configuration:
sudo ufw status verbose
Note: Docker can sometimes ignore UFW rules. To tackle this, verify extra settings as explained here.
Step 3: Docker Installation
Docker will be the container system running NocoBase. Install Docker by running these commands:
Setup dependencies and Docker's GPG key:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install ca-certificates curl gnupg
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg \
| sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
Add Docker repository:
echo \
"deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) \
signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] \
https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(. /etc/os-release && echo $VERSION_CODENAME) stable" \
| sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
Install Docker Engine and compose-plugin:
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli \
containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin -y
Check installation:
sudo docker run hello-world
If you see the "Hello from Docker!" message, Docker is ready.
Step 4: Installing Caddy for Automatic HTTPS
Caddy simplifies HTTPS configuration since it handles SSL certificates automatically from Let's Encrypt.
Important: Before configuring Caddy with your domain, make sure you have pointed your domain's A record (for IPv4) and AAAA record (for IPv6) to your server's IP addresses. Without proper DNS configuration, Caddy won't be able to issue SSL certificates.
Install Caddy:
sudo apt install -y debian-keyring debian-archive-keyring apt-transport-https curl
curl -1sLf 'https://dl.cloudsmith.io/public/caddy/stable/gpg.key' \
| sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/caddy-stable-archive-keyring.gpg
curl -1sLf 'https://dl.cloudsmith.io/public/caddy/stable/debian.deb.txt' \
| sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/caddy-stable.list
sudo apt update
sudo apt install caddy -y
Edit the Caddyfile configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/caddy/Caddyfile
Replace the contents with your domain name for automatic HTTPS:
yourdomain.com {
reverse_proxy localhost:3000
}
Save the file (Ctrl+O, Enter, Ctrl+X) and restart Caddy:
sudo systemctl restart caddy
Step 5: Running NocoBase with Docker Compose
We're going to use Docker Compose with PostgreSQL as the database. First create a directory for NocoBase and navigate to it:
mkdir ~/nocobase
cd ~/nocobase
Create compose.yml:
nano compose.yml
Add the following content:
networks:
nocobase:
driver: bridge
services:
app:
image: nocobase/nocobase:latest-full
restart: always
networks:
- nocobase
depends_on:
- postgres
environment:
# The application's secret key, used to generate user tokens, etc.
# If APP_KEY is changed, old tokens will also become invalid.
# It can be any random string, and make sure it is not exposed.
- APP_KEY=CHANGE_ME_TO_A_RANDOM_SECRET
# Database type, supports postgres, mysql, mariadb
- DB_DIALECT=postgres
# Database host
- DB_HOST=postgres
# Database port
- DB_PORT=5432
# Database name
- DB_DATABASE=nocobase
# Database user
- DB_USER=nocobase
# Database password
- DB_PASSWORD=CHANGE_ME_TO_A_SECURE_PASSWORD
# Timezone
- TZ=UTC
volumes:
- ./storage:/app/nocobase/storage
ports:
- "3000:80"
postgres:
image: postgres:16
restart: always
command: postgres -c wal_level=logical
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: nocobase
POSTGRES_DB: nocobase
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: CHANGE_ME_TO_A_SECURE_PASSWORD
volumes:
- ./storage/db/postgres:/var/lib/postgresql/data
networks:
- nocobase
Make sure to replace the placeholder values:
APP_KEY: generate a random string (at least 16 characters) for session securityCHANGE_ME_TO_A_SECURE_PASSWORD: use a strong password in both theappandpostgresservices
Save the file and deploy NocoBase:
sudo docker compose up -d
Docker pulls the NocoBase and PostgreSQL images and runs them in background mode. NocoBase takes a couple of minutes to fully start up as it initializes the database on first launch.
You can watch the startup progress with:
sudo docker compose logs -f nocobase
Wait until you see that the application has started before proceeding.
Step 6: Accessing Your Self-Hosted NocoBase Instance
Visit your domain (or server IP) in any web browser. Your NocoBase instance should now load successfully.
NocoBase uses default login credentials on first boot: admin@nocobase.com with password admin123. Make sure to change these right after your first login!
After logging in, you'll see the NocoBase admin interface where you can start building your applications, installing plugins, and creating data models!
Security Recommendations
Public servers should always be secure. The following practices are recommended:
- Regularly apply updates and security patches.
- Set strong passwords and control user access.
- Monitor server logs for suspicious activity.
- Keep your Docker images updated.
- Set up regular backups of your PostgreSQL volume. Check out our guide on 4 Easy Ways to Backup Docker Volumes for backup strategies.
Updating your NocoBase Installation
Since we're using the latest tag, updating is straightforward:
cd ~/nocobase
sudo docker compose pull
sudo docker compose up -d
Docker will download the new version and replace your current container. Your data is safe in the PostgreSQL and storage volumes.
Tip: If you want more control over updates, you can pin a specific version tag (e.g.,
2.0.1-full) instead oflatest. Check NocoBase's DockerHub page for available versions.
Cost Comparison with No-Code Platforms
Self-hosting NocoBase typically results in massive savings compared to cloud no-code platforms:
| Service | Monthly Cost | Users Included | Self-Hostable | Data Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retool | $10/user/mo+ | Per seat | Paid only | Vendor servers |
| Airtable | $20/user/mo+ | Per seat | No | US servers |
| Budibase Cloud | $50+ | 5 | Yes (OSS) | EU/US servers |
| Hetzner (self-hosted) | ~€3-5 | Unlimited | Yes | Your servers |
Cost Comparison with Managed Hosting Platforms
If you prefer managed hosting over self-hosting, here's how the costs compare:
| Provider | vCPU Cores | RAM | Disk | Estimated Monthly Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Render.com | 1 | 2 GB | 40 GB | ~€35-€45 |
| Fly.io | 2 | 2 GB | 40 GB | ~€20-€25 |
| Railway | 2 | 2 GB | 40 GB | ~€15-€66* |
| sliplane.io | 2 | 2 GB | 40 GB | ~€9/month flat |
*Note: Railway charges for actually used memory and CPU time. €66 is the max price, actual price might vary.
With self-hosting on Hetzner (as shown in this guide), you can get similar specs for just ~€3/month, but you're responsible for all the setup and maintenance. Managed platforms handle that for you at a higher price point.
Troubleshooting
NocoBase container won't start
Check the logs for errors:
sudo docker compose logs nocobase
Common issues include incorrect database credentials and insufficient memory. Make sure the passwords match in both the NocoBase and PostgreSQL services.
Can't access NocoBase from browser
- Make sure your firewall allows ports 80 and 443
- Verify Caddy is running:
sudo systemctl status caddy - Check if NocoBase is running:
sudo docker compose ps - Ensure your DNS is pointing to your server's IP address
- Give NocoBase a couple of minutes to finish starting up. The initial boot can take some time
SSL certificate issues
Caddy automatically handles SSL certificates, but if you're having issues:
- Make sure your domain DNS is properly configured
- Check Caddy logs:
sudo journalctl -u caddy - Ensure ports 80 and 443 are open and not blocked by your hosting provider
FAQ
Is NocoBase the same as NocoDB?
No! They are completely different projects. NocoDB is a spreadsheet-style database interface (an Airtable alternative). NocoBase is a full no-code/low-code application development platform with a plugin-based architecture for building business apps, CRMs, workflows, and more.
Can I install plugins on self-hosted NocoBase?
Yes! The community edition supports all open-source plugins. You can install them from the NocoBase plugin marketplace directly through the admin interface, or build your own custom plugins.
Is NocoBase free?
Yes! The community edition is completely free to self-host. You only pay for the server infrastructure. NocoBase also offers commercial plugins and enterprise support for teams that need additional features.
Can I use MySQL instead of PostgreSQL?
NocoBase supports both PostgreSQL and MySQL. To use MySQL, change DB_DIALECT to mysql and update the database connection details accordingly. However, PostgreSQL is the recommended option for production environments.
Now you have your own self-hosted NocoBase instance running on Ubuntu 24.04 with PostgreSQL! Start building your business applications, CRMs, and internal tools.
If managing and securing your own server is a bit too much for you, check out how easy it is to deploy a managed instance of NocoBase on Sliplane - it takes just 5 minutes!
Cheers, Atakan